Hip Replacement
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased hip joint is replaced with an artificial joint or prosthesis. This procedure is typically performed to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance the overall quality of life for individuals with hip joint problems.
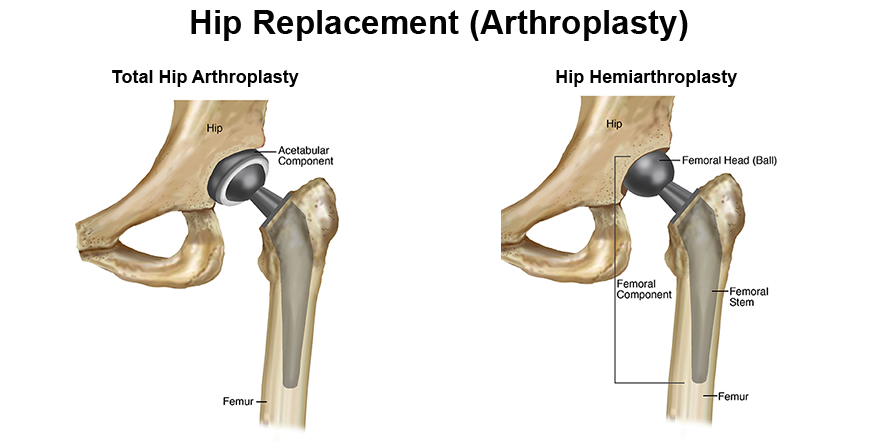
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery :
- Total Hip Replacement (THR): In a THR, both the ball (the femoral head) and socket (the acetabulum) of the hip joint are replaced with prosthetic components.
- Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty): In a partial hip replacement, only the femoral head is replaced, typically due to a fracture or injury.
Factors Leading to Hip Replacement Surgery :
- Osteoarthritis: The most common cause of hip replacement, characterized by the degeneration of hip joint cartilage due to ageing.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that affects the hip joint.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops following a hip injury or fracture.
- Avascular Necrosis: A condition in which the hip joint’s blood supply is disrupted, leading to the death of bone tissue.Other Inflammatory Conditions: Certain inflammatory joint diseases can lead to hip joint damage.
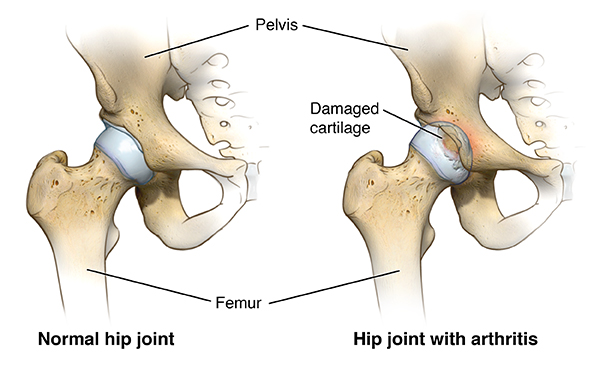
Symptoms and Indications for Hip Replacement :
Common signs of Hip Replacement may include:
- Severe hip pain that restricts daily activities and is not alleviated by conservative treatments.
- Reduced range of motion and stiffness in the hip.
- Instability, limping, and difficulty walking or bearing weight on the affected hip.
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- Comprehensive assessment by an orthopaedic surgeon or hip specialist.
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI, to evaluate the extent of hip joint damage.
- Review of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and impact on daily life.
- Discussion with the patient to confirm that conservative treatments (e.g., medications, physical therapy) have not provided adequate relief.
- The choice between total or partial hip replacement and the specific surgical approach will be determined based on the individual’s unique circumstances and goals for recovery.
