Knee Replacement Surgery in Faridabad
Knee replacement surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased knee joint is replaced with an artificial joint, called a prosthesis. This procedure is performed to relieve pain, improve function, and enhance the quality of life for individuals with severe knee problems.
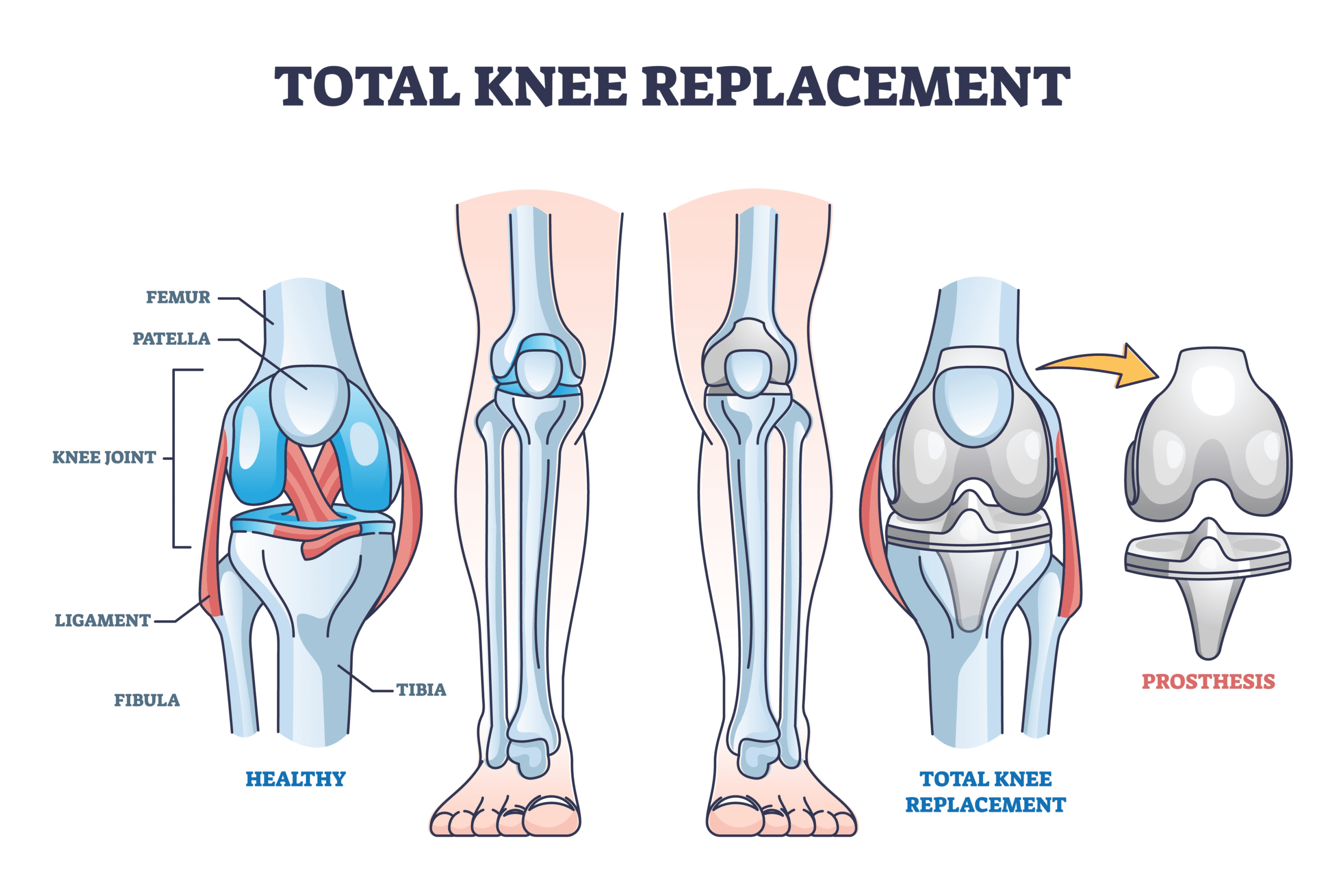
Types of Knee Replacement Surgery :
- Total Knee Replacement (TKR): In a TKR, both the femoral (thigh bone) and tibial (shin bone) components of the knee joint are replaced with prosthetic implants.
- Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): A PKR involves replacing only one part of the knee joint, either the medial (inner), lateral (outer), or patellofemoral (under the kneecap) compartment.
- Bilateral Knee Replacement: Some individuals may require knee replacement in both knees, which can be done in a single surgery or as separate procedures.
Factors Leading to Knee Replacement Surgery :
- Osteoarthritis: The most common reason for knee replacement, typically caused by wear and tear of the joint with aging.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition affecting the knee joint.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops following a knee injury or fracture.
- Other Inflammatory Conditions: Certain inflammatory joint diseases can lead to knee joint damage.
- Osteonecrosis: Death of bone tissue, often due to insufficient blood supply.
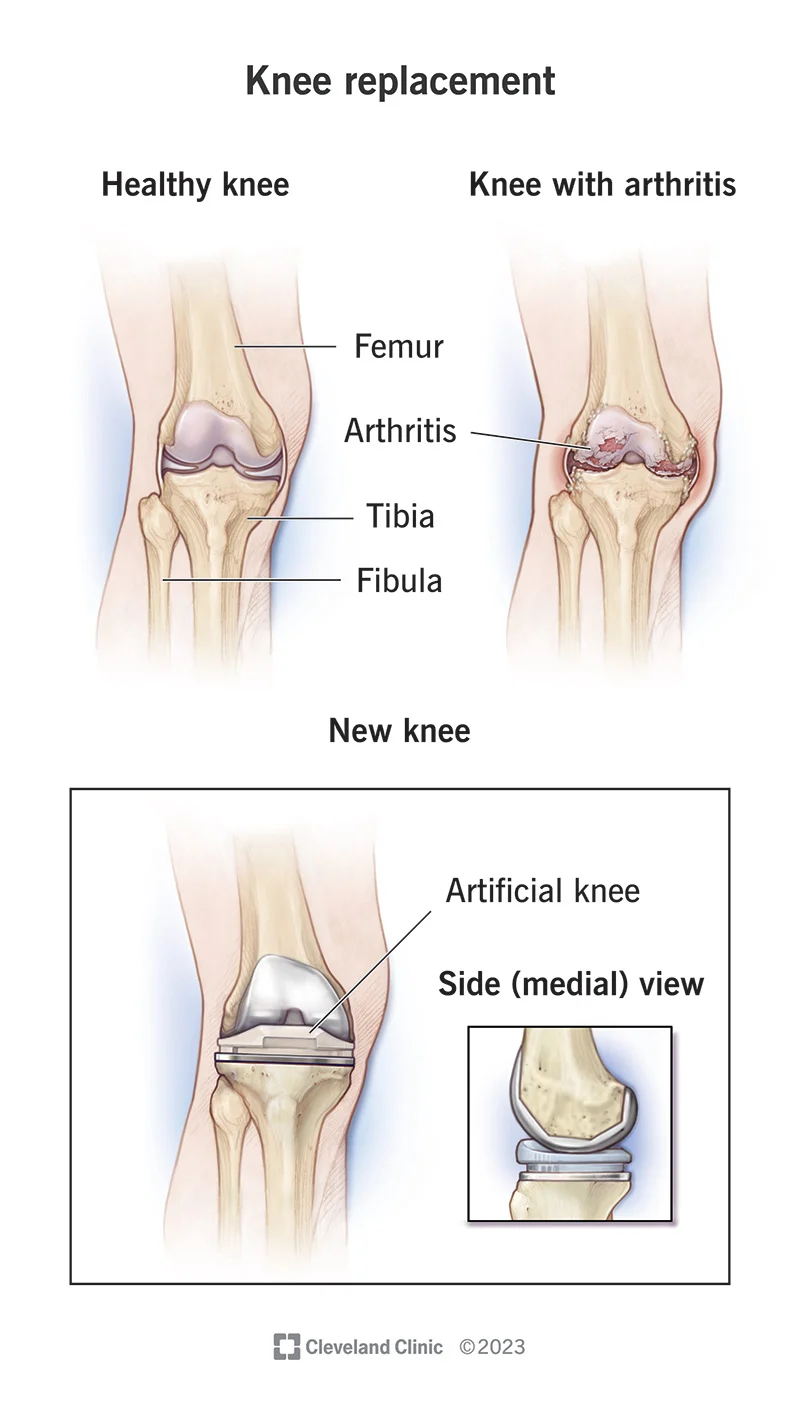
Symptoms and Indications for Knee Replacement :
Common signs of Knee Replacement may include:
- Severe knee pain that limits daily activities and is not alleviated by conservative treatments.
- Reduced range of motion and stiffness in the knee.
- Swelling, instability, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected knee.
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- A thorough evaluation by an orthopaedic surgeon or knee specialist.
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays and MRI, to assess the extent of joint damage.
- Review of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and impact on daily life.
- Discussion with the patient to confirm that non-surgical treatments (e.g., medication, physical therapy) have not provided sufficient relief.
