TFCC Tear Treatment in Faridabad
A TFCC tear, or Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex tear, is an injury that affects the cartilage and ligaments in the wrist, particularly the triangular fibrocartilage. This injury can cause pain, weakness, and limited wrist mobility. Treatment options may include rest, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgery.
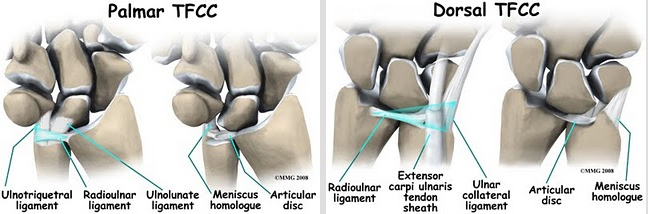
Types of TFCC Tears
- Peripheral Tear: This type of TFCC tear is on the outer edge of the TFCC, closer to the wrist joint’s periphery. Peripheral tears are often less severe and may respond well to conservative treatments.
- Central Tear: Central TFCC tears occur in the central portion of the TFCC, closer to the ulna bone. These tears are usually more complex and may require surgical intervention to repair.
- Ulnar-Sided Tear: Ulnar-sided TFCC tears affect the portion of the TFCC near the ulna bone, leading to pain and instability on the little finger side of the wrist.
- Palmar Tear: A palmar TFCC tear occurs on the side of the TFCC facing the palm. It can be a more challenging tear to diagnose and treat.
- Dorsal Tear: Dorsal TFCC tears are on the side of the TFCC facing the back of the hand. They can also present unique diagnostic and treatment challenges.
- Combined Tears: Some TFCC tears involve multiple parts of the complex or may extend to other structures in the wrist, making them more complex and requiring specialized treatment.
Factors Included :
Several factors can contribute to the development of a TFCC tear (Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex tear). These factors may include:
- Trauma: Sudden injuries, such as falls on an outstretched hand or direct impact to the wrist, can lead to TFCC tears.
- Repetitive Stress: Activities that involve repeated wrist motion, such as sports or manual labor, can put stress on the TFCC and increase the risk of tears.
- Degenerative Changes: Conditions like arthritis or joint degeneration can weaken the TFCC over time.
- Anatomical Variations: Some individuals may have variations in wrist anatomy that make them more prone to TFCC injuries.
- Overuse: Excessive and repetitive use of the wrist, especially in activities that involve loading the wrist joint, can contribute to TFCC tears.
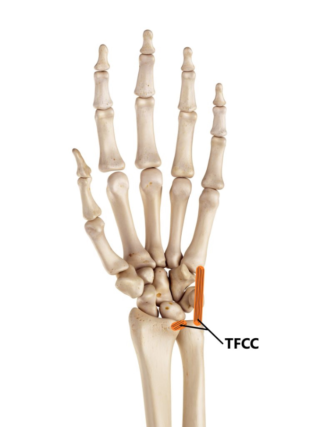
What are the common Symptoms of TFCC Tear ?
The symptoms of a TFCC tear (Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex tear) can vary in severity, but commonly include:
- Pain: Pain is often felt on the ulnar (pinky) side of the wrist, particularly when moving the wrist or gripping objects.
- Weakness: You may experience weakness in your wrist, making it difficult to perform certain activities that require wrist strength.
- Clicking or Popping: Some individuals hear or feel a clicking or popping sensation in the wrist when moving it.
- Limited Range of Motion: TFCC tears can lead to a reduced range of motion in the wrist, making it challenging to flex, extend, or rotate the wrist
- Swelling: Swelling around the wrist joint is a common symptom of a TFCC tear, and it may be accompanied by warmth and redness.
- Instability: The wrist may feel unstable, and you might have difficulty supporting heavy objects or performing weight-bearing activities.
- Tenderness: The area over the TFCC may be tender to the touch.
- Catching or Locking: In some cases, the wrist may catch or lock in certain positions, causing discomfort.
How to diagnose TFCC Tear?
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the wrist will be conducted. This includes checking for tenderness, swelling, range of motion, and stability of the wrist. Imaging: To confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of the TFCC tear, imaging studies may be ordered. These can include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI is a valuable tool for visualizing soft tissue structures like the TFCC and can provide detailed images of the wrist.
- X-rays: X-rays are often done to rule out other potential causes of wrist pain or to check for any bony abnormalities.
- Arthroscopy: In some cases, a minimally invasive procedure called wrist arthroscopy may be performed. During arthroscopy, a small camera is inserted into the wrist joint to directly visualize the TFCC and any tears.
